What is ERPS Ring?
ERPS (Ethernet Ring Protection Switching) is a ring protection protocol developed by the ITU, also known as G.8032. It is a link-layer protocol specifically applied to Ethernet rings. It can prevent the broadcast storm caused by the data loop when the Ethernet ring network is complete, and when a link on the Ethernet ring network is disconnected, it can quickly restore the communication between various nodes on the ring network.
How does ERP work?
Link Health Status:
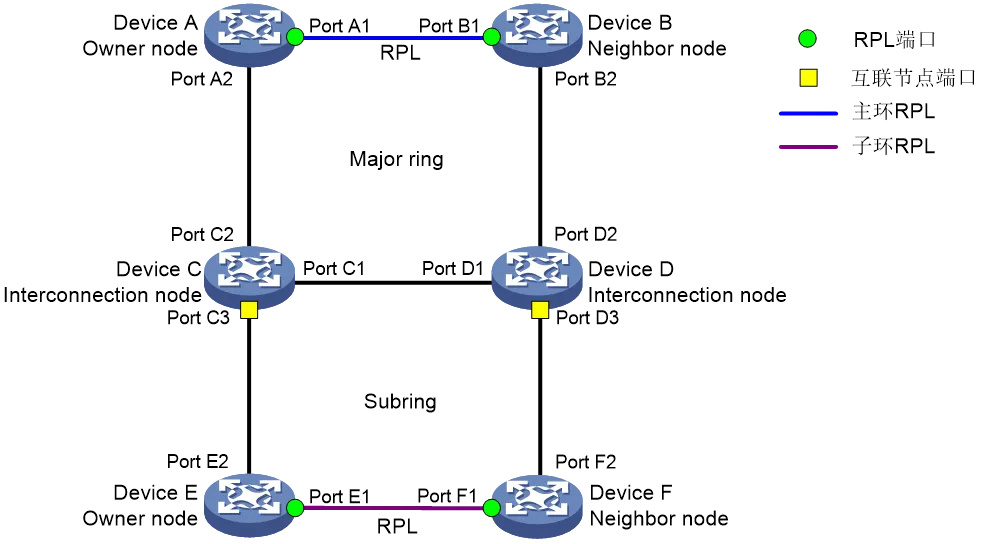
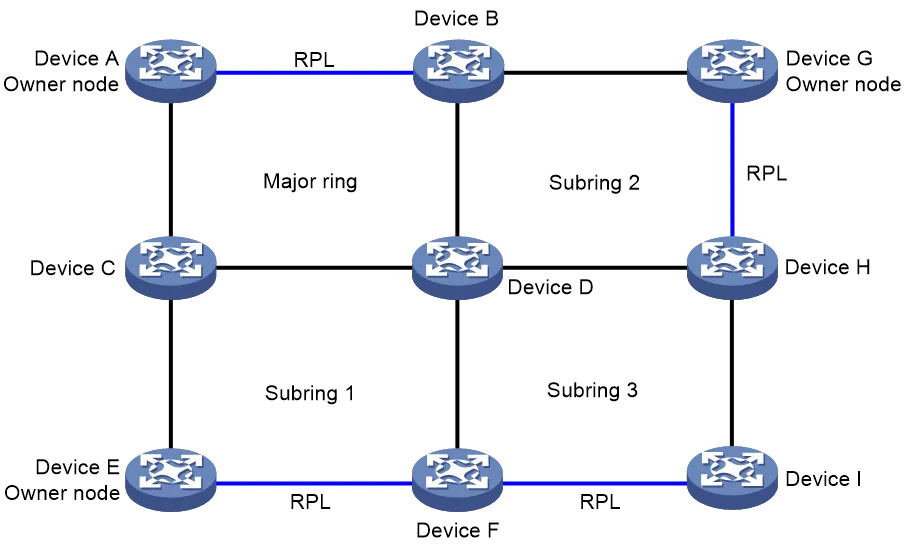
An ERPS ring consists of many nodes. Ring Protection Link (RPL) is used between some nodes to protect the ring network and prevent loops from occurring. As shown in the following figure, the links between Device A and Device B, and between Device E and Device F are RPLs.
In an ERP network, a ring can support multiple instances, and each instance is a logical ring. Each instance has its own protocol channel, data channel, and owner node. Each instance acts as a separate protocol entity and maintains its own state and data.
Packets with different ring IDs are distinguished by destination MAC addresses (the last byte of the destination MAC address represents the ring ID). If a packet has the same ring ID, the ERP instance to which it belongs can be distinguished by the VLAN ID it carries, that is, the ring ID and VLAN ID in the packet uniquely identify an instance.
Link Failure Status:
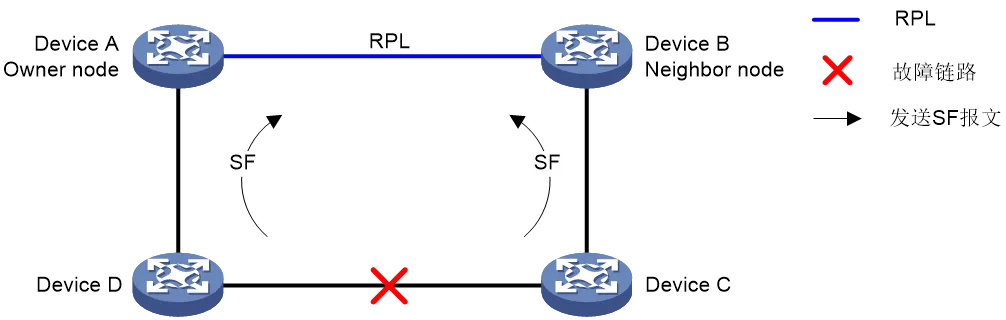
When a node in a link finds that any port belonging to the ERPS ring is down, it blocks the faulty port and immediately sends an SF packet to notify that the other nodes on the link have failed.
As shown in the following figure, when the link between Device C and Device D fails, Device C and Device D detect a link fault, block the faulty port, and periodically send SF messages.
Link Healing Status:
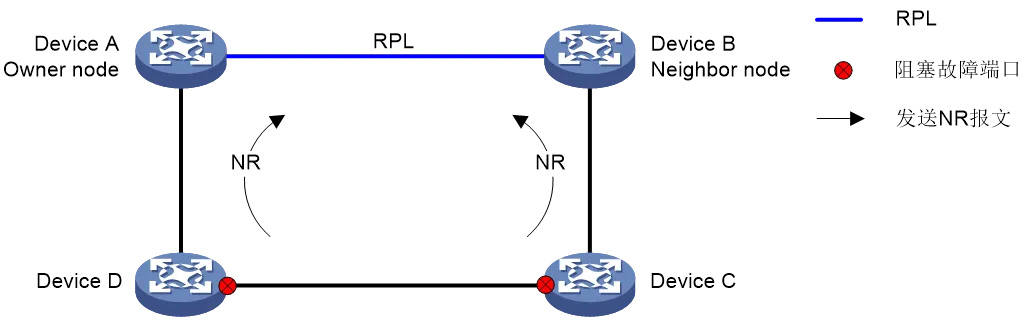
After the faulty link is restored, block the port that was in the fault state, start the guard timer, and send an NR packet to notify the owner that the faulty link has been restored. If the owner node does not receive an SF packet before the timer times out, the owner node blocks the RPL port and periodically sends (NR, RB) packets when the timer expires. After receiving the (NR, RB) packet, the recovery node releases the temporarily blocked fault recovery port. After receiving the (NR, RB) packet, the neighbor node blocks the RPL port and the link is restored.
As shown in the following figure, when Device C and Device D detect that the link between them is restored, they temporarily block the port that was previously in the failed state and send an NR message. After receiving the NR message, Device A (the owner node) starts the WTR timer, which blocks the RPL port and sends (NR, RB) packets to the outside world. After Device C and Device D receive the (NR, RB) message, they release the temporarily blocked recovery port; Device B (Neighbor) blocks the RPL port after receiving (NR, RB) packets. The link is restored to its pre-failure state.
Technical features and advantages of ERPS
ERP Load Balancing:
In the same ring network, there may be data traffic from multiple VLANs at the same time, and ERP can implement load balancing, that is, traffic from different VLANs is forwarded along different paths. The ERP ring network can be divided into control VLAN and protection VLAN.
Control VLAN: This parameter is used to transmit ERP protocol packets. Each ERP instance has its own control VLAN.
Protection VLAN: In contrast to the control VLAN, the protection VLAN is used to transmit data packets. Each ERP instance has its own protection VLAN, which is implemented by configuring a spanning tree instance.
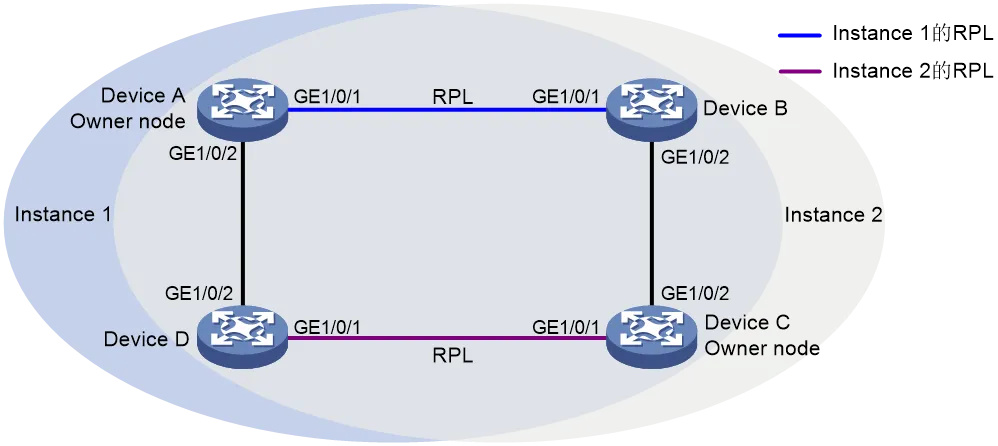
By configuring multiple ERP instances on the same ring network, different ERP instances send traffic from different VLANs, so that the topology of data traffic in different VLANs in the ring network is different, so as to achieve the purpose of load sharing.
As shown in the figure, Instance 1 and Instance 2 are two instances configured in an ERPS ring, the RPL of the two instances is different, the link between Device A and Device B is the RPL of Instance 1, and Device A is the owner node of Instance 1. The link between Device C and Device D is the RPL of Instance 2, and Decive C is the owner of Instance 2. RPLs of different instances block different VLANs to implement load balancing in a single ring.
High level of security:
There are two types of VLANs in ERP, one is the R-APS VLAN and the other is the data VLAN. R-APS VLAN is used only to transmit protocol packets from ERPS. ERP only processes protocol packets from R-APS VLANs, and does not process any protocol attack packets from data VLANs, improving ERP security.
Support multi-loop intersection tangent:
ERP supports adding multiple rings in the same node (Node4) in the form of tangent or intersection, which greatly increases the flexibility of networking.
All ring network industrial switches support ERPS ring network networking technology, which greatly improves the flexibility of networking, and the fault convergence time is ≤ 20ms, ensuring the high stability of front-end video data transmission. In addition, it supports the use of single-core optical fiber to form an ERPS ring network to ensure that there is no bottleneck in video data upload, and at the same time saves a lot of optical fiber resources for customers.
What does ERP do?
ERP technology is suitable for Ethernet ring topologies that require high reliability and high availability. Therefore, it has been widely used in finance, transportation, industrial automation and other fields. In the financial field, key business systems need to ensure high reliability and real-time data transmission, so ERP technology is widely used. In the transportation industry, where network reliability and connectivity are critical to public safety, ERP technology can help improve network stability in the data exchange system of ring network topology. In industrial automation systems, ERP technology can help the network to be more reliable, thus ensuring the normal operation of the production line. ERPS technology can help enterprise networks achieve rapid switching and fault recovery, ensure business continuity, and achieve millisecond-level link recovery, so as to effectively ensure the quality of user communication.
Post time: Jul-13-2024

